Bioremediation oil spills
AState Key Laboratory of Frozen Soil Engineering, Cold and Arid areas Environmental and Engineering Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Lanzhou 730000 (China)bLanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Lanzhou 730000 (China)cDepartment of Geography, Harbin university, Harbin 150086 (China)
Citation: Yang, S. Z., Jin, H. J., Wei, Z., He, R. X., Ji, Y. J., Li., X. M. and Yu, S. P. 2009. Bioremediation of oil spills in cold surroundings: A review. Pedosphere. 19(3): 371–381.
ABSTRACT
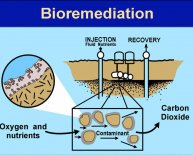
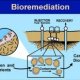
Oil spills became a significant issue in cool conditions aided by the ever-increasing resource exploitation, transportation, storage, and accidental leakage of oil. A number of practices, including real, chemical, and biological practices, are used to recover spilled oil through the environment. Bioremediation is a promising selection for remediation since it is effective and financial in removing oil with less excessive ecological problems. However, it is a relatively slow process in cool regions together with degree of success will depend on some elements, like the properties and fate of oil spilled in cold environments, and also the major microbial and ecological restrictions of bioremediation. The microbial elements feature bioavailability of hydrocarbons, size transfer through the cellular membrane, and metabolic limits. As for the ecological limits in the cold regions, the emphasis is on soil temperatures, freeze-thaw procedures, air and vitamins access, poisoning, and electron acceptors. There were several instances of success into the polar areas, particularly in the Arctic and sub-Arctic areas. However, the challenges and constraints for bioremediation in cool environments stay huge.