Environmental impact of Deepwater Horizon oil spill
On April 20, 2010, a mixture of dirt, seawater and fuel from methane hydrates erupted from oil fine of this Deepwater Horizon oil rig. The Deepwater Horizon had been a semisubmersible platform seeking oil deposits. Once it found oil, the workers up to speed the rig capped the newly-drilled fine in preparation to move on looking for even more oil.
The oil rig floated much more than 5, 000 legs (1, 524 meters) of water inside gulf. The fine it self went further - over 13, 000 feet (3, 962 yards). The workers on rig as well as the businesses involved - BP, Transocean and Halliburton - state there had been some disagreement in the capping procedure. Usually, at the very least two concrete plugs would be poured and hardened into the piping before removing the drilling mud from the fine bore. The dirt assists block sudden bursts of gasoline and oil.
Ultimately, engineers made a decision to remove the mud before incorporating a second cement connect. a burst of gas hurried up the pipeline and caused an enormous explosion, killing 11 of the employees in the process. Oil begun to put from the fine in huge volumes - quotes of this level of oil spilling into the gulf are priced between 12, 000 to 60, 000 drums of oil a day. A barrel of oil is equivalent to 42 gallons (159 liters).
A BP document disclosed that in a worst case scenario, the oil fine could pour around 100, 000 drums of oil in to the ocean per day. At the time of this writing, 2 months following the preliminary explosion, oil continues to be gushing in to the gulf coast of florida. Oil data recovery efforts have paid off, but not eliminated, the quantity of oil hitting the environmental surroundings.
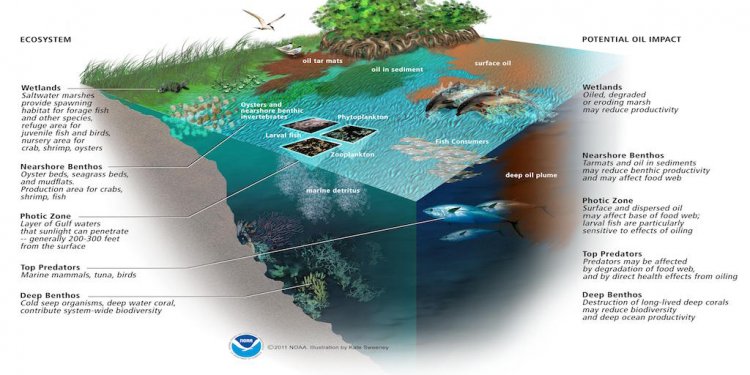
What's the ecological influence? It really is difficult to estimate. Because oil spill took place in deep-water miles from land, the oil spill actually influencing the shore exactly the same way the Exxon Valdez disaster did years ago. A number of the oil clumps together to make tar balls. These balls of tar can wash up on beaches and impact the area wildlife. Plumes of oil tend to be drifting several thousand foot underneath the sea's area. The impact this oil could have on deep sea life isn't fully understood. You can find complex ecosystems deep under the ocean that might perish completely as a result of being inundated with oil.
State and national governments are spending huge amount of money so that they can retain the oil pour while designers try to look for an approach to stop it. BP abandoned an effort to plug the oil well with dirt - the so-called top kill process - when engineers began to concern yourself with the integrity of the well bore itself. In the event that well bore features leaks along its size, oil could continue to spill even when the utmost effective is connected with dirt.
Engineers estimate that a fix towards the issue may not be possible until August - four months after the initial surge. With a permanent fix eluding BP and the federal government, the next reaction should you will need to capture the maximum amount of oil from the fine that you can before it may spread through the entire environment. According to Admiral Thad W. Allen of the U.S. Coast Guard, the purpose of the effort will be have methods in place effective at siphoning down 60, 000 to 80, 000 barrels of oil every day.
It may be many years or decades before we realize the degree associated with the environmental damage the Deepwater Horizon accident caused. While rescue attempts will work challenging reduce the results, it is clear that there surely is no chance to approximate the damage this oil spill is going to do to the environment.